

China, the world's second-largest economy, is facing significant economic headwinds. Recent developments suggest a heightened level of concern from the Chinese government over the economic challenges facing the country.s
China, the world's second-largest economy, is facing significant economic headwinds. Recent developments suggest a heightened level of concern from the Chinese government over the economic challenges facing the country. The People's Bank of China (PBOC) has announced new emergency measures which include a cut to the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) in a bid to stabilize the situation.
On February 5, the PBOC is set to cut to the RRR by 50 basis points. This move is notable for two reasons: it is double the typical 25 basis point cut, and it deviates from the usual process of signaling such a move through the State Council before a formal announcement by the PBOC.
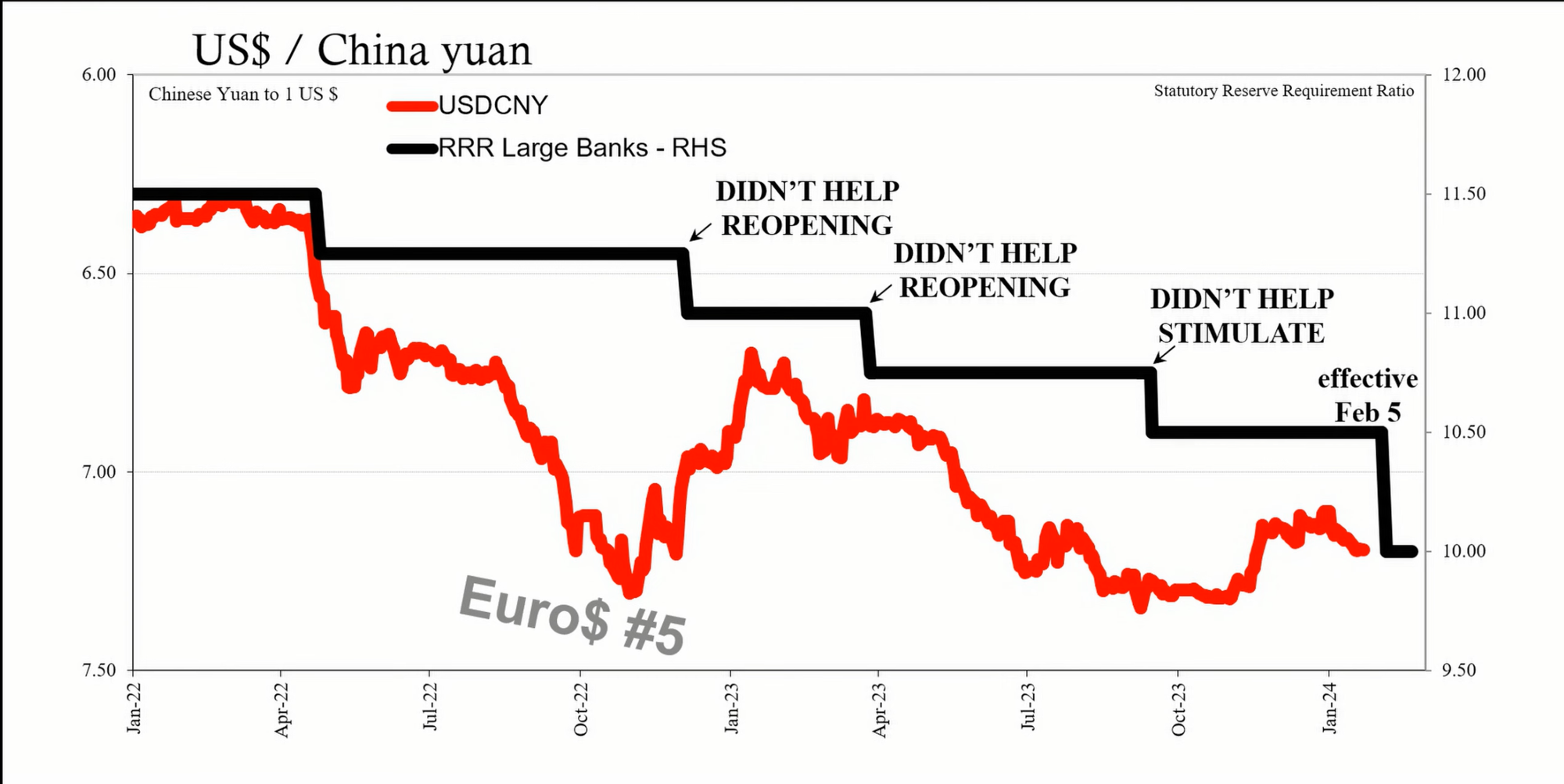
The RRR cut is designed to allow Chinese banks to use more of their cash holdings rather than keep it in reserve. The intention is to encourage banks to lend more and stimulate the economy. However, historical patterns suggest that RRR cuts are typically associated with periods of economic distress and are not necessarily stimulative. These cuts have occurred during challenging times, such as the euro dollar cycles of 2015-2016 and 2018-2019, and more recently in 2022.
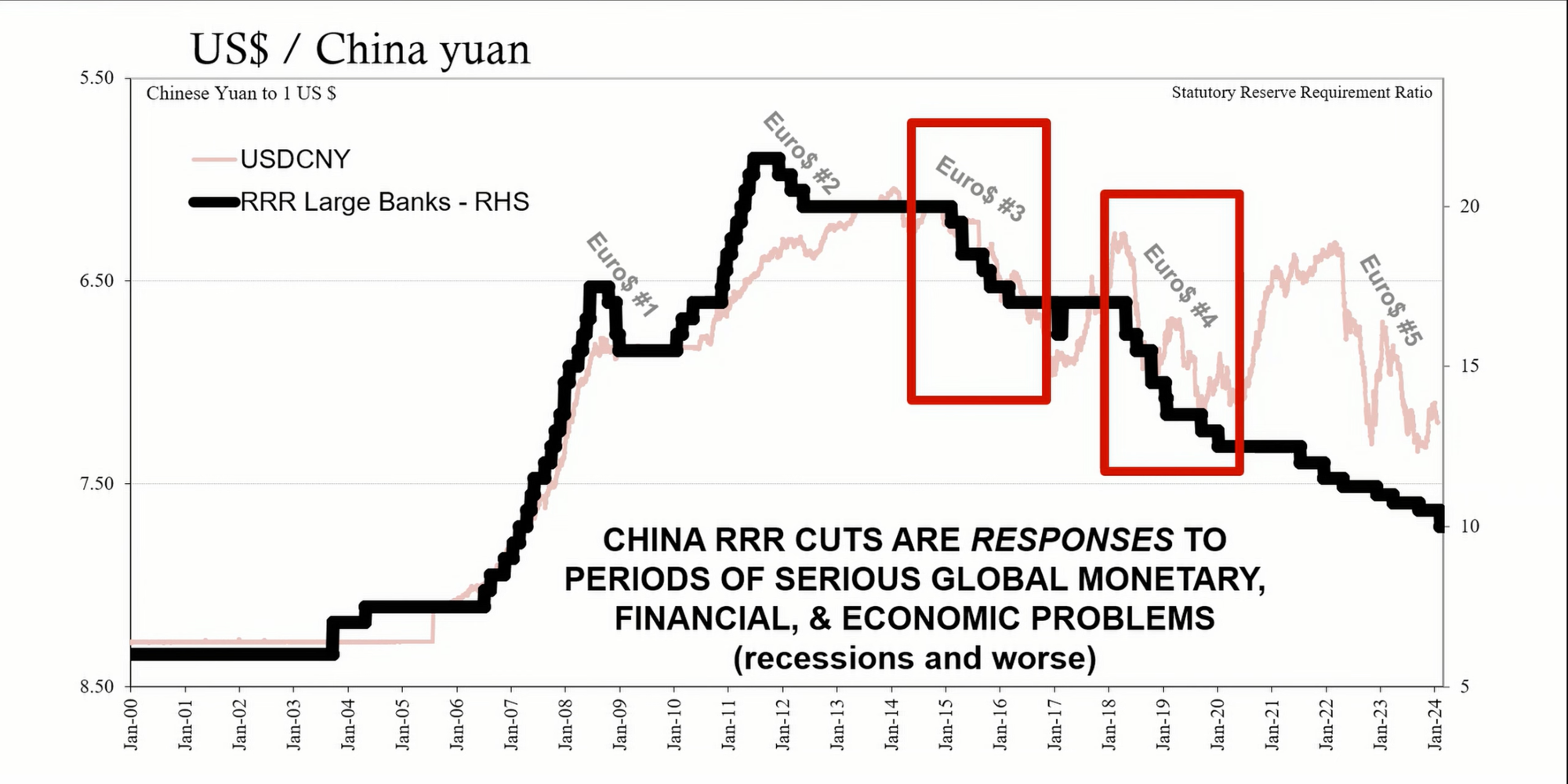
A Bloomberg quote suggests that announcing an RRR cut in advance implies a lack of other effective tools to address market turbulence. This move is seen as a response to a declining stock market and broader economic deterioration.
PBOC Governor Pan Gongsheng also indicated future plans to assist "high quality" real estate developers with funding. This statement suggests that the real estate issues may be affecting more stable developers and not just those previously in distress.
Chinese authorities are reportedly planning to mobilize substantial funds from both offshore and local sources to stabilize the stock market. This includes a proposed 2 trillion yuan from state-owned enterprise accounts and at least 300 billion yuan through domestic channels. Measures such as a short-selling ban on Chinese stocks also indicate a growing unease from policymakers.
Assessing the situation on a scale of calm to disorderly unwind, the recent actions by Chinese authorities suggest a shift from moderate concern to a higher level of alert, potentially moving from a level five to a six or seven, given the lack of economic response to stimulus efforts and the real estate market's difficulties.
Key indicators for assessing the seriousness of China's economic challenges include the Chinese yuan's exchange value, repo rates, and the Shibor (Shanghai Interbank Offered Rate). A weakening yuan, increasing repo rates, and an elevated three-month Shibor rate could signal further liquidity concerns and risk aversion among banks.
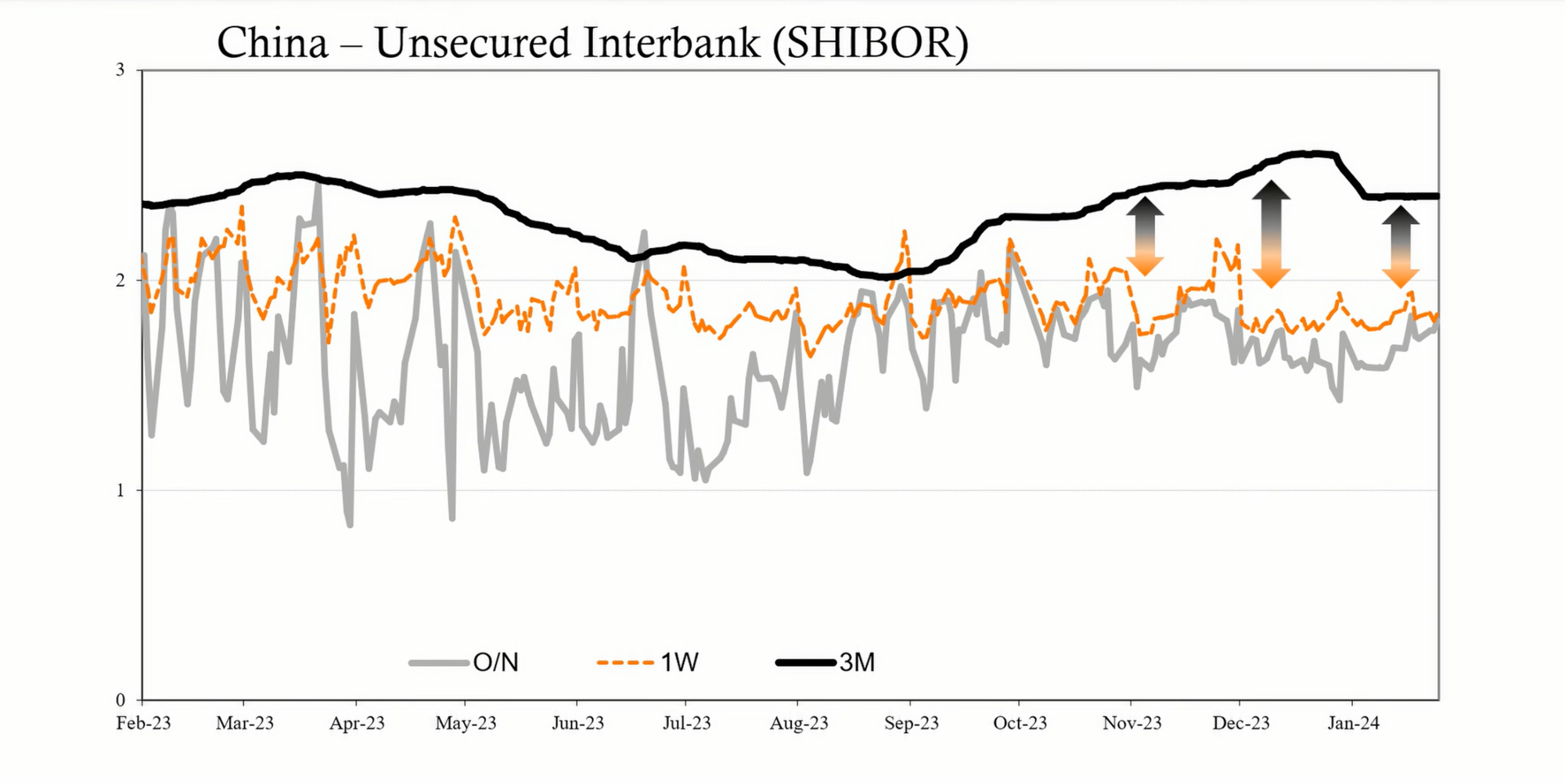
The PBOC's recent RRR cut and other market interventions indicate a heightened state of concern regarding China's economic trajectory. While still a risk rather than a certainty, there is a realistic possibility of a disorderly unwind that the Chinese authorities are trying to prevent. Observers will continue to monitor financial indicators, government responses, and the real economy for signs of either stabilization or further deterioration. The implications are significant not only for China but for global trade, financial markets, and geopolitical stability.