
Navigating the cost of health insurance in any state can be overwhelming. With prices varying significantly across the country, it is crucial to understand why certain states have higher premiums. For example, in 2024, the most expensive states for health insurance include Vermont, where premiums can reach up to $841 per month.
One reason for these high costs is the varying healthcare regulations and market conditions in each state. States like West Virginia and Wyoming also see high premiums, with costs averaging $824 and $802 monthly, respectively. Understanding these price differences helps consumers make better decisions about their healthcare options.
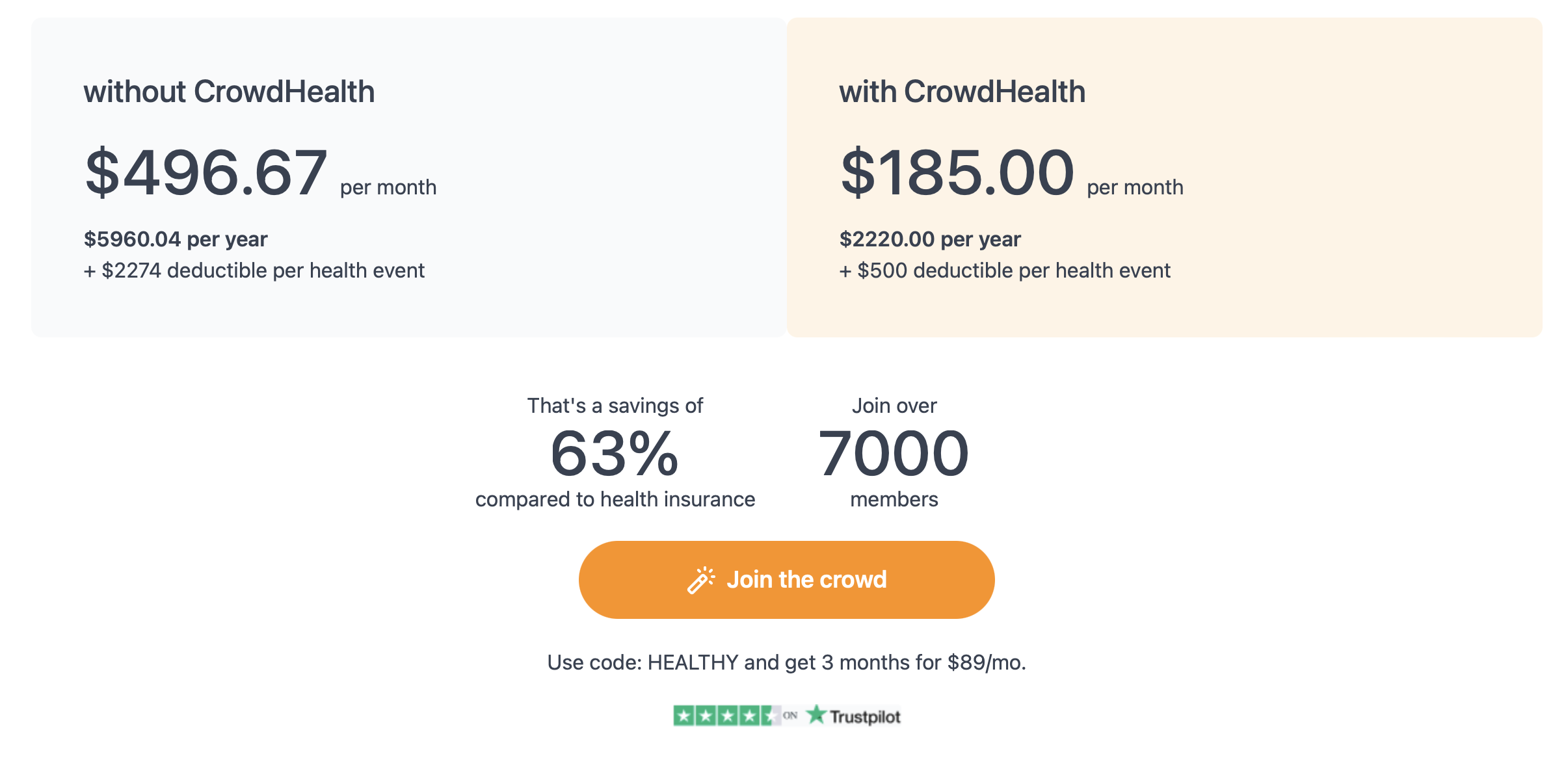
Comparing traditional health insurance with alternative models like CrowdHealth is essential to finding the best fit for individual needs. CrowdHealth offers a different approach, potentially providing more affordable options depending on the state. By examining the costs and benefits, individuals can make more informed choices about their health coverage.
Health insurance costs vary widely across the United States. Several factors determine these costs, including location, age, and plan type. Here’s a closer look.
Vermont has the country's most expensive health insurance premiums, at an average of $841 per month. Residents face high costs due to fewer insurers and a smaller risk pool.
West Virginia follows closely, with premiums averaging $824 per month. Economic factors and a higher prevalence of chronic conditions contribute to these high costs. Wyoming's monthly premiums are about $802, influenced by its rural landscape and limited healthcare providers.
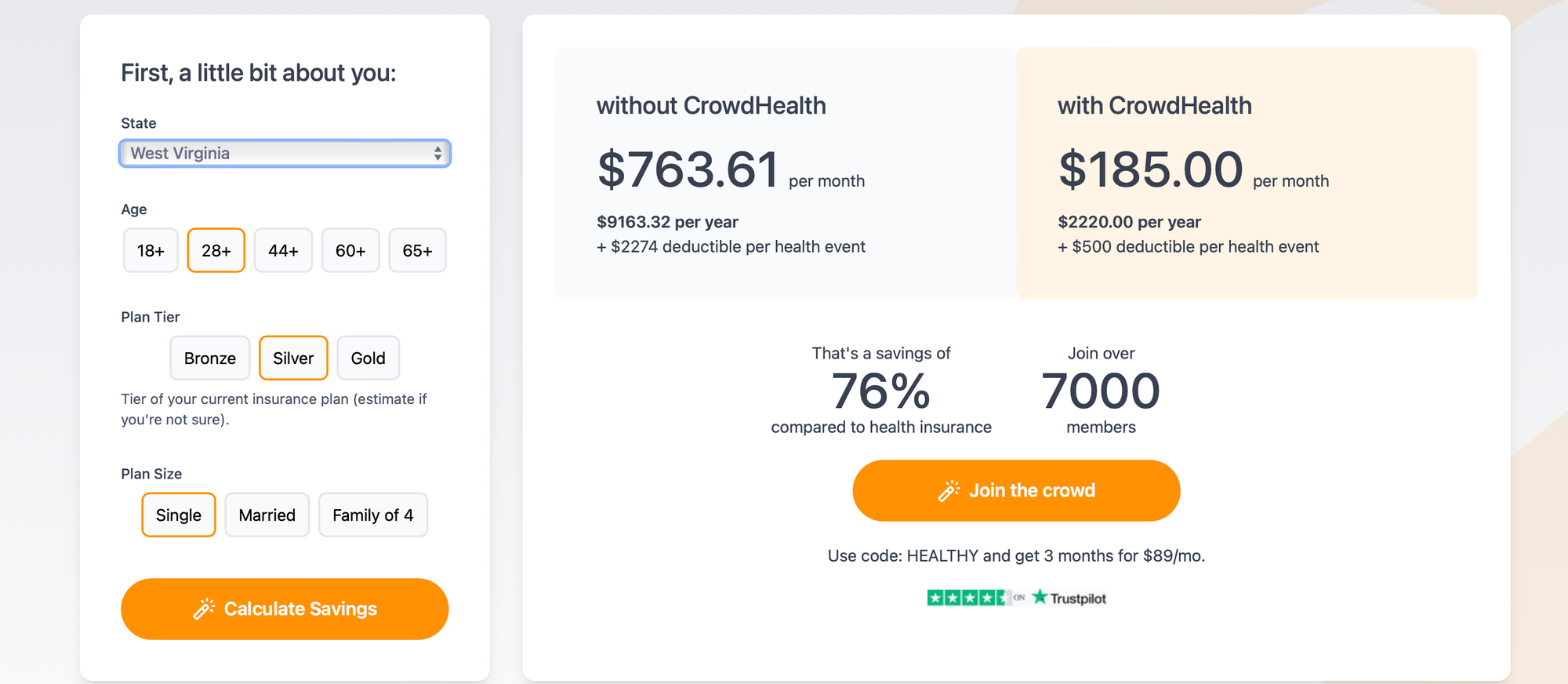
States like North Carolina, Florida, and Texas also experience significant costs, primarily due to higher demand and fewer coverage options. The South generally sees higher premiums due to economic disparities and regional health challenges.
Factors such as state regulations, population health, and the number of insurers are crucial in determining health insurance costs across different states. Understanding these dynamics can help consumers make informed decisions about their coverage options.
CrowdHealth offers a unique approach to managing medical expenses by leveraging crowdfunding. This can be a game changer for those struggling with high traditional health insurance premiums in various states.
CrowdHealth is a platform that allows people to pool their money to pay for medical expenses. Instead of paying high premiums to health insurance companies, members contribute a fixed monthly fee, such as $50. This helps reduce costs significantly, as noted in the Forbes article.
This system can bypass the usual administrative costs many insurance companies have, which can take up to 25% of a final medical bill, as reported by Forbes. The focus is on community support and direct payments, rather than profit-driven care.
We are done crowdfunding for the year.
— CrowdHealth (@JoinCrowdHealth) December 28, 2023
3,506 submitted to the community for crowdfunding
3,506 funded by the community
We had some doozies. Brain surgery, cancer cases, motor vehicle accidents, NICU babies, a whole bunch of MSK surgeries, and a host of other large events.… pic.twitter.com/isPNN9ue9O
You Can Check out Crowdhealth vs your state here.
Health insurance costs vary significantly across states due to several factors, including state regulations, the competitive landscape, and the percentage of the insured population.
Several factors contribute to these variations. These include the cost of medical services, state regulations, the health of the population, and administrative costs. States with higher healthcare costs often have higher premiums.
State regulations can dictate what services must be covered, which can increase costs. Some states have more stringent insurance requirements, resulting in higher premiums. Others may have policies that support more affordable plans.
States like Vermont and West Virginia have some of the highest healthcare costs. Vermont has an average premium of $841 per month, while West Virginia's is $824. These costs are influenced by provider fees and the local cost of living. Wyoming also ranks high with $802 per month.
Yes, the cost of living plays a role. States with higher living costs often see higher insurance premiums. Income levels also affect affordability and what residents are willing to pay for coverage. States with higher incomes usually have higher premiums due to the demand for premium healthcare services.
When fewer insurance providers exist in a state, there is less competition, which can lead to higher premiums. In contrast, states with many providers and competitive markets often have lower premiums due to the increased competition driving prices down.
States with higher insured rates tend to have more stable and predictable healthcare costs. This can lower premiums because the risk is spread across a larger population. Conversely, states with lower insured rates may see higher premiums due to the increased financial risk for insurers.








